Effects of N, P and K Fertilizer on Crude Fat Content in Rice
In addition to protein, fat content is another important nutritional quality indicator of rice. With the increase in the quality of rice, people began to pay attention to the level of crude fat in rice. The research on improving the crude fat content of rice was firstly paid more attention in quality breeding. The study of Zhai Zubai showed that the fat content was quantitative and the heritability was relatively high. Tang Liyun et al. reported that using non-high-quality products with low fat content as parents is not conducive to improving rice fat content. Huang Yingjin et al. showed that the high fat content of rice is the specific shape of some famous rice varieties. The above studies indicate that the content of crude fat has a certain relationship with the taste of rice, but there has been no report on the effect of fertilization on the crude fat content of rice. This experiment studied the effects of different nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizer application rates on crude fat content in rice, in order to provide a theoretical reference for high-quality cultivation of rice.
1 Materials and Methods
1. 1 Nitrogen fertilizer test
1.1.1 The test materials for the test were Wuyujing No. 3, Wulianjing No. 1 and Xieyou No. 57. The application of nitrogen fertilizer is urea.
1.1.2 Test design The test set up four different application rates of different types of preserved fertilizer, namely pure nitrogen 0, 5, 10, 15 kg/667m2 (hereinafter referred to as N0, N5, N10, N15 respectively). Early stage of fertility application of pure nitrogen 10kg/667m2, according to 8:2 as base fertilizer and tiller fertilizer use. The experiment was set up for 3 repetitions. Randomized blocks were arranged with a row spacing of 30 cm and a hole spacing of 10 cm. Each field plot was embedded with a plastic film to prevent cross-fertilization of the fertilizer. Other agronomic management measures were the same as in Daejeon, with an area of ​​6 m2. The test was conducted in 2003 at the Agricultural Research Institute of Gangba Farm, Jiangsu Province. The former crop was wheat, and the soil was lake black soil. The sample taken before planting was analyzed, containing 1.80% organic matter and 0.12% total nitrogen. 8 mg/kg。 Hydrolysis of nitrogen 81. 60 mg / kg, available phosphorus 14. 95 mg / kg, quick-acting potassium 158. 8 mg / kg.
1.2 Phosphate fertilizer and potash fertilizer test
1. 2. 1 The tested varieties are Shanyou 63 and Wuyujing No. 3.
1. 2. 2 Experimental design This experiment was conducted using potted plants, with 5 pots per pot, 3 pots per pot, 1 pot per hole from Shanyou 63, and 2 pots per hole from No. 3 in Wuyujing. During the whole growth period, pure nitrogen 2 g/pot was applied, and 7:3 was used as base fertilizer and flower-fertilizer. Phosphorus and potash fertilizer treatment can be divided into two methods: potassium application without phosphorus and phosphorus application without application of potassium. The amount of P2O5 and K2O used was 5 levels, which were 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 g per pot, represented by P0, P2, P4, P6, P8, and K0, K2, K4, K6, and K8, respectively. During the topdressing period, draw out the fallen 4 leaves. The diameter and height of the pots were all 30 cm. Each pot was loaded with 18 kg of soil. The soil was sandy loam soil. The soil was thoroughly mixed before loading and sampling analysis was performed. The soil hydrolyzable nitrogen content was 367 mg/kg and the available phosphorus content was 63. The 6 mg/kg, available potassium content was 562 mg/kg. The experiment was conducted in 2003 in the Lianyungang City Agricultural Technology Extension Center.
1. 3 Measurement methods
The crude fat content can be determined by the SZF-06A fat analyzer or the SZF-06B fat analyzer. Although there are slight differences in the functions of the two different models, the fat content can be determined.
2 Results and Analysis
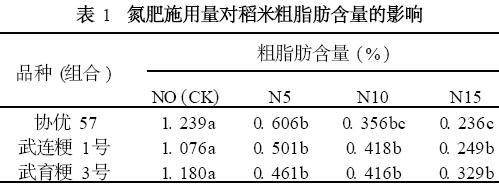
2.1 Effect of nitrogen fertilizer application on crude fat content in rice
It can be seen from Table 1 that the effects of different nitrogen fertilizer application amounts on the three varieties (combinations) were basically the same in the later period, and the crude fat content decreased with the increase of the amount of nitrogen fertilizer application, and there was a significant difference from the control, but in the N5, N10 The differences between N15 and N15 fertilization treatments were relatively flat, and the differences between the N15 and N15 treatments were different. Among them, Wuyujing No. 3 and Wulianjing No. 1 were not significant. Only N5 and N15 treatments of Xieyou 57 were 0. 606% and 0. 236%, the difference is significant. Between the varieties, with the increase of nitrogen fertilizer, the decreasing trend of crude fat content was different. Among them, the crude fat content of 4 treatments in Wuyujing No. 3 was 1.180%, 0.461%, 0.416%, 0 respectively. 329%, the downward trend is slightly slower than the other two varieties (combination). The above results indicate that the late application of nitrogen fertilizer will significantly reduce the crude fat content of rice, and the crude fat content of indica rice is more sensitive to nitrogen fertilizer than indica rice, but with the increase of nitrogen fertilizer application, the downward trend will slow down.
Effect of Potassium Fertilizer Application on Crude Fat Content in Rice
The results in Table 2 show that the K2 processed crude fat content of Wuyujing No. 3 was 0.704% slightly lower than that of the control 0. 722% except that the other treatments were all higher than the control. The control ratio was significantly different (except for K4 treatment); Wuyujing No. 3 increased with the increase of potassium application amount, and Shanyou 63 significantly decreased at the K6 level. The above results show that applying a certain amount of potassium fertilizer can increase the crude fat content of rice.
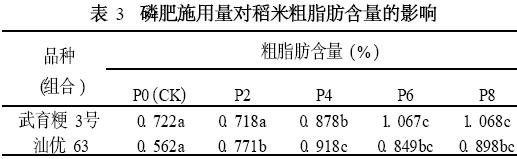
Effect of fertilizer application amount on crude fat content in rice
The results in Table 3 show that the crude fat content of the two cultivars (combinations) was higher than that of the control, except that the difference between Wuyujing No. 3 treated by P2 and the control was not significant, and the rest were significantly different. Below the level of P4, the content of crude fat increased significantly. After Wuyujing 3 was higher than P2, the content of crude fat increased significantly with the increase of phosphorus application. The above results show that the application of phosphate fertilizer can significantly increase the crude fat content of rice.
3 Summary and discussion
Huang Yingjin and other researchers believe that the fat content of rice has a more important impact on the taste of rice than other quality traits. Within a certain range, increasing the fat content of rice can significantly improve the taste quality of rice. Studies have shown that as rice grades of rice varieties increase, the higher the fat content, the better the palatability and aroma of rice. Wu Changming et al found that rice fat content was significantly correlated with rice taste, appearance and other traits, while protein content had a significant negative effect, indicating that increasing crude fat content and moderately controlling protein content were beneficial to improve rice food quality. Therefore, in the selection of rice varieties and cultivation of high-quality rice, the index of crude fat content in rice should be taken into account and strengthened.
In this experiment, the crude fat content of the tested varieties (combinations) decreased with the increase of nitrogen fertilizer levels, indicating that topdressing nitrogen fertilizers later reduced crude fat content. The addition of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers can increase the crude fat content. Therefore, a proper reduction in the amount of nitrogen fertilizers and an increase in the amount of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers will help improve the crude fat content and thus improve the quality of rice taste. Different types of crude fat content showed different results under different levels of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium treatments, and Wuyujing No. 3 had poorer sensitivity to nitrogen response than Wulianjing No. 1 and Xieyou 57, and Wuyu Chang 3 is more sensitive to phosphorus and potassium than Shanyou 63. Therefore, in the cultivation of high-quality rice, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizers should be formulated according to different varieties.
Door Frame Roll Forming Machine, this machine
is specially designed for making door frame for various types doors like
shutter door mainly. This type machine working speed could reach 25m/min. And
for the material thickness is from 0.5-2.5mm.After roll forming by our production line, we could make very smooth and beautiful door frame without any scratch on surface. This metal door frame production line is composed by the following elements: De-coiler, feed & leveling device, punching machine with holes punching moulds, main roll forming machine, cutter, run-out table, etc.This cold roll forming line adopts accumulator and PLC controller to generate a fast punching and shearing speed.

Door Frame Roll Forming Machine
Door Frame Roll Forming Machine, Aluminum Door Frame Roll Forming Machine, Metal Door Frame Roll Forming Machine
Zhongtuo Roll Forming Machinery Co., ltd , https://www.frameforming.nl